Have you ever noticed? When you brew coffee hot and place it on the desk after a while, you will find that the coffee in the glass is gradually changed from hot to warm until the time passed for a while, the coffee in the glass disappeared. And do you wonder? How is the heat from the coffee in the glass gone?
I have an answer for you.  Because the heat from the coffee in the glass is replaced by the temperature from the surrounding area including the coffee mug and the work desk itself, causing the heat of the coffee to disappear.
Because the heat from the coffee in the glass is replaced by the temperature from the surrounding area including the coffee mug and the work desk itself, causing the heat of the coffee to disappear.
This principle of refrigeration system is the same as the cooling system that heats away from the object or the temperature inside the room and replaces it with the cooling system. In addition to that, the cooling system also helps maintain the temperature that is suitable for use as well.
If you are interested in making a cooling system, this article will help you understand. Working principle of refrigeration system and help you to know the principles and equipment that are easier to understand.
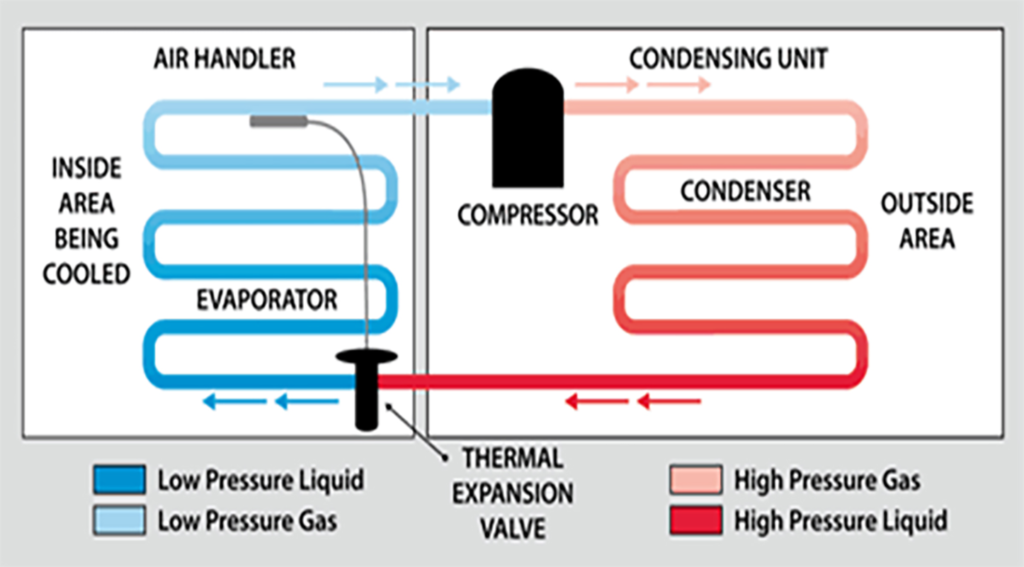
Key Components of a Refrigeration System:
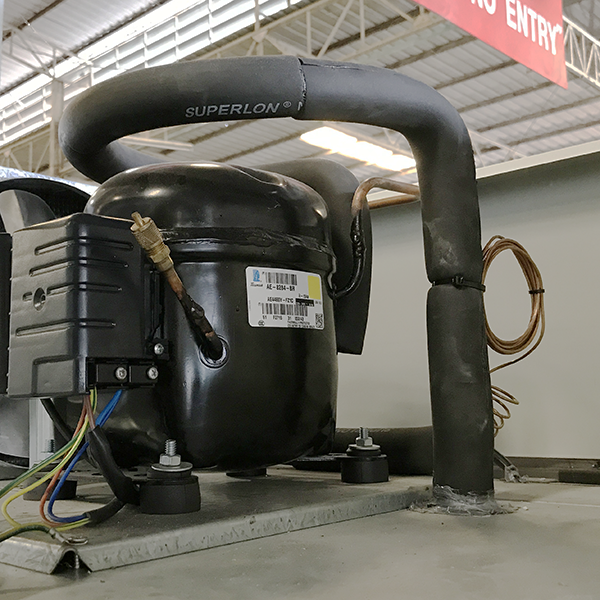
The cooling device that is in the condensing unit has the principle that it can be cooled by absorbing heat from the desired area to replace it in the cooling area. There are 5 basic devices which have important functions in the cooling system
1) Evaporator
Evaporator is an important part that acts as a heat exchanger from the area that needs cooling which will act alongside the refrigerant or air cleaner by making the refrigerant boil until it becomes vapor and can absorb heat from the surface of the evaporator.
Notice that most cooling coils have air duct systems or fans which has the function of blowing air or sucking wind to help cool the cooling coil and the air flowing through this evaporator will be absorbed by the heat to change into coldness.
2) Compressor
When the refrigerant in the steam state runs out of the coil Will have a low pressure and have a vapor status of the refrigerant from a very high temperature because the vapor state of the refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding air flowing through and will continue flowing to the vaporizer The function of the vaporizer in refrigeration system is to absorb the refrigerant in a vaporized form. To compress to a higher pressure before condensing to the condenser or heating coil
3) Condenser
The refrigerant, when traveling from the vaporizer machine, will have a high temperature and high pressure. The condenser of refrigeration system is a device that acts to cool the heat from the refrigerant to help condense the refrigerant that has a vapor status to return to liquid again.
the vaporizer machine, will have a high temperature and high pressure. The condenser of refrigeration system is a device that acts to cool the heat from the refrigerant to help condense the refrigerant that has a vapor status to return to liquid again.
4) Expansion Valve
The expansion valve in the refrigeration system is the last part of the cooling function to help reduce the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. The pressure of the refrigerant sent from the coil or condenser will flow through the pressure reducing valve which will lower the pressure of the refrigerant. As a result, the refrigerant is ready to evaporate at low temperatures at the next device, which is the cooling coil.
5) Refrigerant
Refrigerants (also commonly referred to as the coolant) is a substance that can change the state from liquid to vapor and from vapor to liquid easily. When the refrigerant changes the state from liquid to vapor, it absorbs heat from nearby areas into the cooling coil and emits heat when changing the state to  liquid again at the coil.
liquid again at the coil.
The properties of the refrigerant must have good stability and long use. With the efficiency of the refrigerant that is not reduced, the price is low, can bring a lot of heat, not ignite, do not explode, do not react with lubricant Not reacting with water has a low volume of gas per unit weight and uses low compressive strength.
Cooling Principle
Current refrigeration, there are many types depending on the need for use, including refrigerators, freezers, cold rooms, ice plants, air conditioners. Cooling in general industrial factories with the same purpose is reduce the temperature and maintain the temperature as specified.
The principle of the initial cooling is the same. Making the substance which is the cooling medium (Refrigerant) change status by using latent heating in order to allow the intermediate cooling agent to change its status from liquid to vapor resulting in decreasing temperature in that area which means that the area will be cold.
Start the cooling process from absorbing heat with an evaporator or cooling coil. Entering the heat that this refrigerant absorbs will cause the refrigerant solution to heat and change from vapor to liquid. This process, the refrigerant will absorb heat from the surrounding area which the latent heat of vaporization of the refrigerant receives heat from various objects near the coil by means of thermal conductivity convection or heat radiation causing this refrigerant to have a high temperature and low pressure.
High temperature refrigerant, this vapor state will be sent to the compressor, which will compress to have higher pressure before forwarding to the condenser or heating coil to cool the heat from the refrigerant and condense the refrigerant in the vapor state to return to the liquid again before forwarding to the Expansion Valve (the pressure reducing valve) to lower the pressure of the refrigerant so that the refrigerant is ready to evaporate at low temperatures at the next device, which is the coil and will continue to work like this according to the cooling cycle of the refrigeration system.
Industries that use cooling systems
The cooling system is an important part that helps in the treatment of raw materials. Or products in various industries to help extend the duration of those products for longer storage and to maintain the cost of production because the cooling from the cooler helps to inhibit the growth of bacteria that causes product spoilage and also helps extend the shelf life of products or food for longer.
1. Food processing
Pasteurization process such as the production of milk or ice cream by heating the milk at 70-80 degrees Celsius. After that, bring to cool quickly and keep at 2-3 degrees Celsius to maintain the quality of the milk before bringing sell to the fermentation process (Fermentation) Curing process (Mellowing) that must be done under the temperature of 5-15 degrees Celsius.
2. Food Storage
Freezing fresh food to preserve freshness, such as vegetables, fruits, meats, to extend the shelf life of food by soaking in a cold room with a temperature below freezing, which reduces the spread of bacteria which is easy to make food rotten.
3. Industrial process production
The cooling system (refrigeration system) is used for manufacturing processes in many industrial plants such as industrial, chemical, petrochemical, oil refinery and gas separation plants.
4. Cooling for transportation
Mobile cooling room system to maintain product quality during delivery to maintain freshness, such as cold rooms on cargo ships. Or a cold room used to transport products to other provinces.
5. Air condition
Air conditioning systems are widely used today. From cars, houses, buildings to industrial work. In addition to cooling, it also works with humidity control systems, air filters, air circulation or ventilation to get fresh cool air.